Resources
BPMN 2.0
Business Process Model and Notation 2.0
In today’s digital landscape, process automation is no longer a luxury, it’s a necessity. The key to successful automation lies in a common language that both business departments and IT can understand and use. BPMN 2.0 is this language. Our intensive online training is specifically designed to show you how to create precise, executable process models that form the foundation for your digitalization and automation initiatives.
What is BPMN 2.0 and Why is it so Important?
BPMN 2.0 (Business Process Model and Notation) is a globally recognized standard from the Object Management Group (OMG), an international organization that develops standards for object-oriented programming. The current version, 2.0, was released in 2011. Think of BPMN as a universal language for visualizing business processes. Much like musical notes make a melody understandable to any musician, BPMN provides a clear and uniform representation of workflows—comprehensible to everyone involved, from business stakeholders and IT experts to executive management.
The primary purpose of BPMN is to bridge the gap between business process design and technical implementation. Thanks to its standardized notation, processes can not only be visualized and analyzed but also directly automated in workflow management systems. This makes BPMN 2.0 an indispensable tool for digitalization and process automation in any organization.
You can find more information about the standard directly from the Object Management Group (OMG).
How Does BPMN Improve Collaboration Between Business and IT?
This is one of the greatest advantages of BPMN, a point consistently emphasized by leading providers like Camunda, Flowable and others. BPMN establishes a common visual language, ensuring clear and unambiguous communication.
-
Eliminating Misunderstandings: Business departments think in terms of processes, while IT thinks in code and systems. BPMN diagrams translate business requirements into a structured format that developers can directly understand and use as a blueprint for implementation. This reduces errors and time-consuming revisions.
-
Accelerating Development: When processes are fully designed and approved by all parties before coding begins, development teams can focus on what matters most: implementing the business logic. Development cycles are streamlined, and the time-to-market for new digital solutions is drastically reduced.
-
Fostering Innovation: Close collaboration and a shared understanding help uncover knowledge gaps. Teams can work together to develop more holistic and innovative solutions because both business needs and technical possibilities are considered from the very beginning.
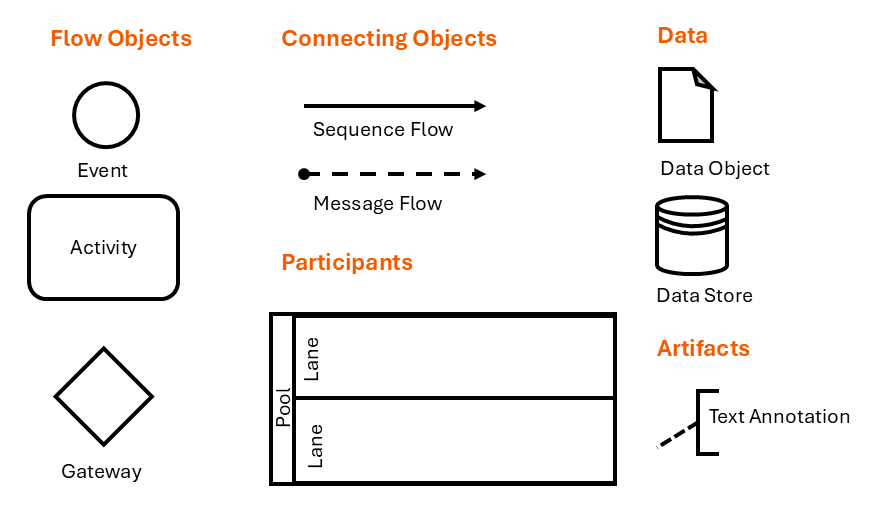
What are the Core Symbol Groups in BPMN 2.0?
The power of BPMN lies in its manageable set of symbols that can be combined to create complex process diagrams. For automation, the Flow Objects are particularly crucial. They are connected by Connecting Objects and organized into areas of responsibility called Swimlanes.
The Main Categories at a Glance:
-
Flow Objects: These describe the behavior within the process.
-
Events: What triggers a process, what interrupts it, and what ends it?
-
Activities: What tasks and work steps are performed?
-
Gateways: How does the process flow split and merge?
-
-
Connecting Objects: These link the Objects together.
-
Sequence Flow: Shows the order of activities.
-
Message Flow: Represents communication between different processes.
-
-
Participants: These assign activities to areas of responsibility.
-
Pools: Represent process conductors (e.g., organizations, departments).
-
Lanes: Subdivide pools into specific process participants (e.g., roles or actors).
-
-
Artifacts: These provide additional information about the process.
-
Data Objects: Show what data is used in the process.
-
Annotations: Allow for free-text comments.
-
How Do Events Control the Process Flow?
Events are the triggers of a business process. They are depicted as circles and signal that something has happened. There are three main types:
-
Start Event: A single, thin-lined circle. Every process begins with a start event. It marks the point at which the process is initiated, e.g., “Order received.”
-
Intermediate Event: A double, thin-lined circle. It occurs during the process and can influence the flow, e.g., “Wait for customer response” or “Send notification after 3 days.”
-
End Event: A single, thick-lined circle. It signals the completion of a process path, e.g., “Order completed.”
For automation, the types of events, represented by icons inside the circle, are especially relevant. For example, an envelope signifies a message event (receiving/sending an email), while a clock represents a timer event.
What are Activities and What Role Do They Play?
Activities represent the work that is performed in the process. They are shown as rounded rectangles. For example, an activity can be a simple task or a complex, reusable sub-process.
-
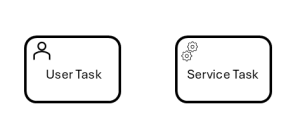
Task: The most granular form of an activity that is not broken down further. Example: “Review invoice.” In automation, these can be either manual or automated steps. A small user icon denotes a User Task (manual task), while a gear icon represents a Service Task (an automated system call, e.g., an API request).
-
Sub-Process: A complex activity that itself consists of a sequence of activities, gateways, and events. It is identified by a small plus symbol within the rectangle. This helps to keep complex processes clear and allows for the graphical representation of end-to-end processes that span multiple departments and systems.
How Do Gateways Direct the Process Flow?
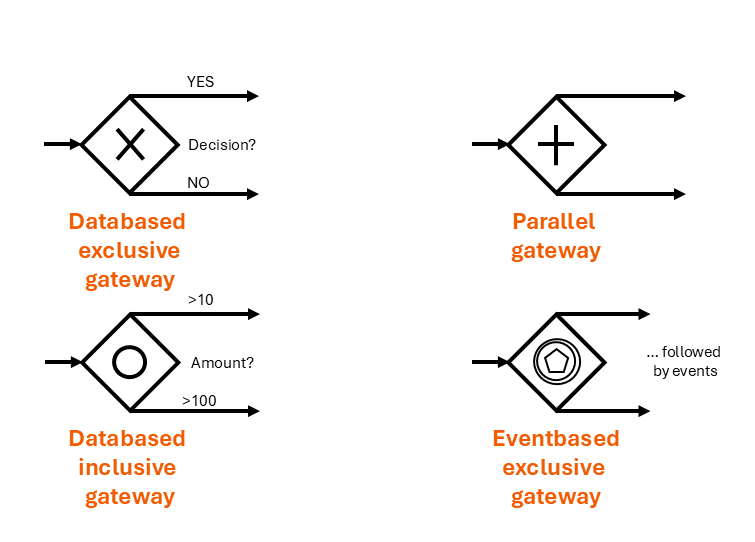
Gateways, represented by diamonds, are the critical control points in a process. They split the process path (splitting) or merge it back together (joining). Choosing the right gateway is essential for the process logic and automation.
Databased Exclusive Gateway: The “either-or” decision. Only one of the outgoing paths can be taken. A classic example is checking “Invoice amount > $1,000?”. If yes, follow path A; if no, follow path B. It is represented by a diamond, optionally with an “X” inside.
Parallel Gateway: The “and” gateway. All outgoing paths are activated simultaneously and independently. It is used when multiple tasks must be performed in parallel, e.g., “Check credit score” AND “Check inventory.” The symbol is a diamond with a plus sign.
Databased Inclusive Gateway: The “one or more” decision. At least one, but potentially multiple, of the outgoing paths can be activated based on fulfilled conditions. For example, a customer might want to receive an order confirmation via both email and SMS. The symbol is a diamond with a circle inside.
- Eventbased exclusive Gateways: An event-based gateway directs the process flow to the specific path determined by whichever of the subsequent events occurs first, invalidating all other alternative paths.
Conclusion: Why is BPMN 2.0 the Key to Success in Process Automation?
BPMN 2.0 is much more than just a tool for drawing pretty diagrams. It is the lingua franca of process optimization and the decisive lever for a successful digital transformation. The arguments are compelling:
Holistic Transparency: BPMN provides a clear end-to-end view of complex workflows. This knowledge is retained within the company, even when employees change roles or leave.
Efficiency and Performance Improvement: Visualization mercilessly exposes bottlenecks, redundancies, and sources of error. Processes can be systematically streamlined and improved, leading directly to higher performance.
Agile and Iterative Implementation: BPMN perfectly supports agile methodologies. Teams can quickly create a viable core product (Minimum Viable Product, MVP) based on a simple model and then improve and expand it iteratively using data.
Future-Proofing through Standardization: As an open standard, BPMN is not tied to a specific technology vendor. The knowledge gained is transferable, and the notation is flexible enough to orchestrate future technologies like AI and agent-based systems.
Anyone looking to sustainably digitize, agilely develop, and intelligently automate business processes today cannot afford to ignore the power and clarity of BPMN 2.0.
Why Choose Our BPMN 2.0 Seminar?
Our live online training, led by experts with extensive practical experience, focuses on the technical application of BPMN. You will learn how to model processes in such a way that they can be directly converted into automated workflows. We move beyond pure theory and use hands-on exercises to give you the skills to bridge the gap between process design and IT implementation.
Mastering BPMN 2.0
€1790
net price, no VAT includedBook your spot today and take the first step towards becoming a proficient process modeler with BPMN 2.0!