Resources
DMN 1.6
Decision Model and Notation 1.6
DMN (Decision Model and Notation) is a global standard for visually modeling and automating business decisions. It provides a common language for defining the “if-then” logic that drives choices within a business process. By separating these rules from the process flow (often modeled in BPMN), it bridges the gap between business experts and IT. This allows companies to manage complex decision logic in intuitive formats, like decision tables. Ultimately, DMN makes your decision-making transparent, agile, and directly executable by software.
What is DMN and Why is it Essential for Business Decisions?
DMN (Decision Model and Notation) is a global standard published by the Object Management Group (OMG), the same consortium that maintains BPMN. Introduced to complement BPMN, DMN provides a common language for modeling and executing business decisions. While BPMN diagrams the flow of a process, DMN specifies the logic behind the decisions within that flow.
Imagine a business process where a loan application needs to be approved. BPMN would model the steps: “Receive Application,” “Check Eligibility,” “Notify Applicant.” DMN, however, defines the precise rules for the “Check Eligibility” step—for example, specifying how a credit score, income, and loan amount combine to produce a “Go” or “No-Go” decision.
The primary purpose of DMN is to separate complex business rules from the process flow. This makes decision logic transparent, manageable by business users, and directly executable by a decision engine. It is a cornerstone for achieving intelligent automation and ensuring consistent, agile, and auditable decision-making.
For more official information, visit the Object Management Group (OMG) DMN page.
How Does DMN Bridge the Gap Between Business and IT?
Like its counterpart BPMN, DMN’s greatest strength lies in creating a shared understanding between different departments. It empowers business experts to take ownership of the rules that govern their operations, leading to significant advantages.
-
Empowering Business Users: DMN uses intuitive visual formats, especially Decision Tables, that resemble spreadsheets. This allows business analysts, legal experts, or product managers to model, review, and even update complex decision logic without writing a single line of code.
-
Decoupling Rules from Code: By externalizing business rules from application code, changes no longer require lengthy IT development cycles. Need to adjust a discount rate or update a risk parameter? A business user can modify the DMN model, test it, and deploy it, making the organization incredibly agile.
-
Creating a Single Source of Truth: DMN models serve as a clear, unambiguous, and executable documentation of your business rules. This eliminates ambiguity and ensures that the documented logic is exactly what the system executes, which is crucial for compliance and auditing.
What are the Core Components of a DMN Model?
A DMN model is structured in two primary levels. This layered approach allows for both a high-level overview and a detailed view of the decision logic.
The Two Levels of DMN:
-
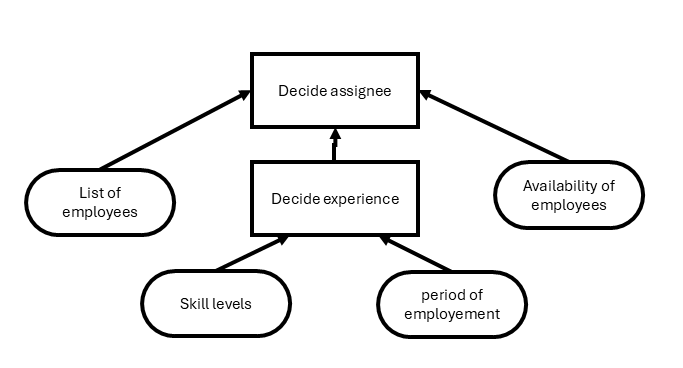
Decision Requirements Level: This provides the “big picture.” It’s visualized using a Decision Requirements Diagram (DRD). The DRD shows the different decisions that need to be made and, crucially, their dependencies—what information, sub-decisions, and data are required to make a final decision.
-
Decision Logic Level: This is where the actual rules are defined for each decision shown in the DRD. While there are several ways to express this logic, the most common and powerful method is the Decision Table.
How Do Decision Tables Work?
Decision Tables are the heart of DMN’s decision logic level. They are a precise and easy-to-read way to represent conditional logic (if-then rules). A decision table consists of columns and rows:
-
Columns:
-
Input Columns (Blue/Grey): Represent the conditions or input data (e.g., “Customer Status,” “Order Value”).
-
Output Columns (Green): Represent the outcomes or results of the decision (e.g., “Discount Percentage,” “Shipping Method”).
-
-
Rows: Each row represents a single rule, combining specific input values with a corresponding output.
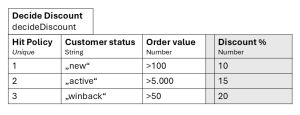
Example: A Discount Rule Table
| Input: Customer Status | Input: Order Value | Output: Discount |
| “Gold” | > $500 | 15% |
| “Gold” | <= $500 | 10% |
| “Silver” | – | 5% |
| “Standard” | > $1000 | 5% |
Another key feature is the Hit Policy, which specifies what to do if multiple rules match the inputs. For example, a ‘Unique’ policy allows only one rule to match, while a ‘First’ policy selects the first matching rule in the table’s order. This adds another layer of precision to the decision logic.
How Do BPMN and DMN Work Together?
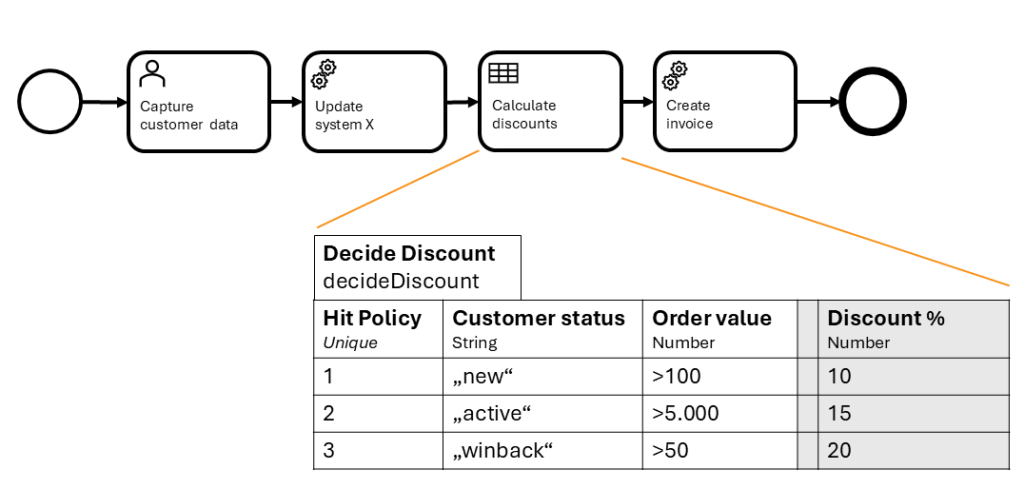
BPMN and DMN are designed to be a powerful team for intelligent process automation. They connect seamlessly within a process model.
-
A BPMN process models the overall workflow.
-
When a decision point is reached, the process flow arrives at a Business Rule Task. This special type of task is marked with a small table icon.
-
This Business Rule Task then calls a DMN model to execute the decision logic.
-
The DMN engine evaluates the rules based on the provided process data and returns the result to the BPMN process.
-
The BPMN process then continues its flow, often using the decision outcome to choose a path at a subsequent Gateway.
This powerful combination allows you to build processes that are both flexible in their flow (BPMN) and intelligent in their logic (DMN).
Conclusion: Why DMN is a Game-Changer for Your Business
DMN is not just another technical standard; it’s a strategic tool for digital transformation. By standardizing and externalizing your business rules, you achieve several critical business outcomes:
-
Unprecedented Agility: Respond to market changes, new regulations, or competitive pressures in hours, not months. Business experts can update the decision logic directly, bypassing slow and costly code changes.
-
Radical Transparency and Consistency: Your decision-making logic is no longer a “black box” hidden in code. It is clearly documented, visible to all stakeholders, and executed consistently across all channels, reducing errors and ensuring fairness.
-
Enhanced Compliance and Auditability: DMN models provide a complete, time-stamped audit trail of every decision. Proving compliance to regulators becomes a simple matter of showing them the model and its execution history.
-
Foundation for Intelligent Automation: Clean, structured decision logic is the perfect foundation for applying more advanced technologies like AI and machine learning. DMN allows you to manage the rules that govern when and how these advanced technologies are applied.
In today’s fast-paced digital world, the ability to make fast, consistent, and intelligent decisions is a key competitive advantage. DMN provides the framework to build this capability directly into the core of your operations.
Why Choose Our BPMN 2.0 Seminar?
Our live online training, led by experts with extensive practical experience, focuses on the technical application of DMN. You will learn how to model rules such a way that they can be directly converted into automated decisions. We move beyond pure theory and use hands-on exercises to give you the skills to bridge the gap between decision design and IT implementation.
Mastering DMN
€749
net price, no VAT includedBook your spot today and take the first step towards becoming a proficient decision modeler with DMN!